All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Effect of Water Sorption on the Mechanical Properties of Surgical Splint Materials: 3D-printed vs Conventional Resin
Abstract
Introduction
Recently, digital technologies have become common in clinical dental practice, which may provide benefits to clinicians and patients. This study investigated how water absorption affected the mechanical properties of three-dimensionally (3D)-printed surgical splint materials used to position bones during orthognathic surgery.
Methods
Two 3D-printing materials, Dental LT Clear (Formlabs) and Splint (SprintRay), as well as a conventional acrylic resin (Unifast III, GC), were purchased for this study. We prepared wire (2 × 2 × 25 mm) and disc-shaped (14 mm diameter and 2 mm in thickness) specimens via 3D-printing or pouring into silicon molds. All materials were subjected to the ISO 4049 three-point bending test, and the water absorptions of samples immersed in artificial saliva for 28 days were calculated as per ISO 10477. Changes in mechanical properties (hardness, and the modulus of elasticity) were evaluated via nanoindentation testing. Chemical parameters were determined using Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR). The data were compared using ANOVA and the Tukey multiple comparisons test.
Results
The bending strengths and elongations of both 3D-printed materials were significantly greater than those of conventional acrylic resin. The FTIR data indicated that the water absorptions of both 3D-printed materials were significantly greater than those of conventional PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate)-based resin. The hardness and elastic modulus values of both 3D-printed materials (obtained using the nanoindentation test) decreased significantly as the immersion period rose; those of the conventional acrylic resin did not.
Discussion
The improved mechanical properties of 3D printed materials would demonstrate greater resistance to the stresses imparted by the muscles associated with functional mandibular movement, while also reducing the risk of splint chipping during intermaxillary fixation. On the other hand, there is concern that the stability of the mechanical properties of 3D printed materials may be compromised by water absorption in moisture-rich environments.
Conclusion
Although 3D-printed materials exhibit superior mechanical properties, their water absorption and extent of degradation on immersion in artificial saliva were higher than those of a conventional PMMA-based resin.
1. INTRODUCTION
Recently, digital intraoral scanning and cone-beam computed tomography have become common in clinical dental practice [1-3]. Three-dimensional (3D) computer-assisted simulation of orthognathic surgery that corrects jaw deformities is more accurate than conventional two-dimensional cephalometric prediction and the use of surgical models; human error is minimized [4, 5].
Surgical splints precisely position the maxilla and mandible during orthognathic surgery. Computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) yield digitally designed, 3D-printed surgical splints; the accuracy of which is high [5, 6]. Traditional acrylic resin splints, hand-fabricated using stone dental models, are less accurate [7-10].
After orthognathic surgery, surgical splints (final splint) usually remain in place for 1 week to 1 month; the splints must be dimensionally and chemically stable, because they may certainly affect the precision of the occlusal positioning. Both polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA; conventional acrylic resin) and the resins used for 3D printing absorb water [11]. This may compromise splint durability via degradation of the mechanical properties.
The purpose of this study was to explore water-mediated degradation of both 3D-printing materials and conventional acrylic resin. This is the first study that reports the water absorption characteristics of 3D-printed materials for surgical splint.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
Two commercial 3D-printing materials, Dental LT Clear (Formlabs, Somerville, MA, USA) and Splint (SprintRay, Los Angeles, CA, USA), and an autopolymerizing PMMA-based resin (Unifast III, GC, Tokyo, Japan) were purchased (Table 1). CAD software (Tinkercad, Autodesk, San Rafael, CA, USA) was used to design rectangular wires of cross-section 2 × 2 mm and length 25 mm, and discs 14 mm in diameter and 2 mm in thickness that were 3D-printed by a digital light processing (DLP) device (Pro 95, SprintRay). The layer thickness was 50 µm and the X/Y resolution was 95 µm. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations, the specimens were initially washed with 99% (v/v) isopropyl alcohol, subjected to multistage automated washing, and dried (Pro Wash/Dry, SpringRay). Post-processing employed a post-curing device (Pro Cure, SpringRay) and proceeded at 30°C for 15 min under a 405-nm light-emitting diode array. The comparative specimens were prepared via thorough mixing of appropriate amounts of the PMMA polymer and MMA (methyl methacrylate) monomer liquid, and this PMMA-based resin mixture was poured into silicon molds.
2.2. Three-point Bending Test
The three-point bending test (n = 10) employed a span size of 12 mm (ISO specification 4049, 2019). Specimens were loaded onto a universal testing machine (EZ Test, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) with a 20-N load cell and subjected to a deflection of at least 4 mm at 1 mm/min, or until fracture. The elastic modulus and the bending strength (the force at bending failure) were calculated using inbuilt software (Trapezium ver. 2, Shimadzu).
| No. | Abbreviations | Main Component | Product Name | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DLC | Methacrylic oligomer | Dental LT Clear | FormLabs |
| 2 | SP | Acrylic Oligomers | Splint | SprintRay |
| 3 | UF | Polymethyl methacrylate | Uni Fast III | GC |
2.3. Water Absorption
All specimens (n = 10/group) were dried in a desiccator containing silica gel (Middle Granule, Kanto Chemical Co. Inc., Tokyo, Japan) for 24 h at 37 ± 1°C, and then in a second desiccator at 23 ± 1°C for 2 h, and weighed using an analytical balance (HR-200, A&D Company, Tokyo, Japan) with an accuracy of 0.1 mg. This cycle was repeated for approximately 3 weeks, at which time constant mass (M1) was obtained. All specimens were then immersed in individual 10-mL plastic vials containing artificial saliva with CaCl2 and NaH2PO4 with a Ca/PO4 for 30 days at 37ºC, then the surface liquid was wiped off using a dry cloth, and weighed (M2). Water sorption (Ws), representing the percentage increase in weight, was calculated using the following formula:
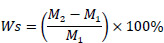 |
2.4. Characterization of Chemical Structure by Fourier-transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Chemical parameters were investigated via FTIR in the attenuated total reflection (ATR) mode using a diamond detector (FT/IR-6600, Jasco, Tokyo, Japan). Spectra were collected from 4,000 to 400 cm-1 at a resolution of 4 cm-1. The spectrum number averaged 32; this ensured a high signal-to-noise ratio. After baseline correction, the spectra were normalized to facilitate comparisons.
2.5. Degradation of Mechanical Properties as Revealed by the Nanoindentation Test
During immersion as described above, all specimens underwent nanoindentation testing on days 0, 1, 3, 7, 14, and 30 to evaluate mechanical properties such as hardness and the elastic modulus (ENT-1100a instrument, Elionix, Tokyo, Japan). A Berkovich-type diamond indenter (a triangular pyramid with a ridge line angle of 115°) was used for the measurements. To investigate the mechanical properties of both the surface and the deep layers, two indentation loads were applied: 10 mN (indentation depth approximately 1,500 nm) and 100 mN (indentation depth approximately 5,000 nm). Ten samples of each material were tested at each of 10 sites. The hardness and elastic modulus were calculated using the inbuilt software that met the ISO 14577-1 guidelines.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses employed SPSS version 22 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Data normality was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk test and by drawing Q-Q plots. The Levene test was employed to evaluate the variance homogeneity across the groups. After confirming these assumptions, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare the mean values across groups, and the Tukey post-hoc test was employed for pairwise comparisons when significant differences were apparent. The level of significance was set to p < 0.05 for all tests.
Power analysis employed G*Power ver. 3.1 with an assumed effect size (f) of 0.4 as suggested by the literature [12-14], an alpha level of 0.05, and a power of 0.80. The analysis included three groups and six repeated measurements; the non-sphericity correction was 0.2 and the correlation among repeated measures was 0.5. The required sample size was 30; the actual power was 0.827.
3. RESULTS
The three-point bending curves in Fig. (1) show that the elastic modulus, bending strength, and elongation (deflection to fracture) of both 3D-printing materials were similar, and significantly greater than those of conventional PMMA-based resin. On immersion in artificial saliva, the water absorptions of both 3D-printing materials increased significantly over time, as shown in Fig. (2), and were significantly greater than those of conventional PMMA-based resin. On FTIR, both 3D-printed materials exhibited an increase in the water peak intensity at 3,600 cm-1, as shown in Fig. (3). The hardness and elastic modulus values of the nanoindentation test decreased significantly with increasing duration of immersion as shown in Fig. (4). The conventional PMMA-based resin exhibited no significant degradation of mechanical properties on immersion.
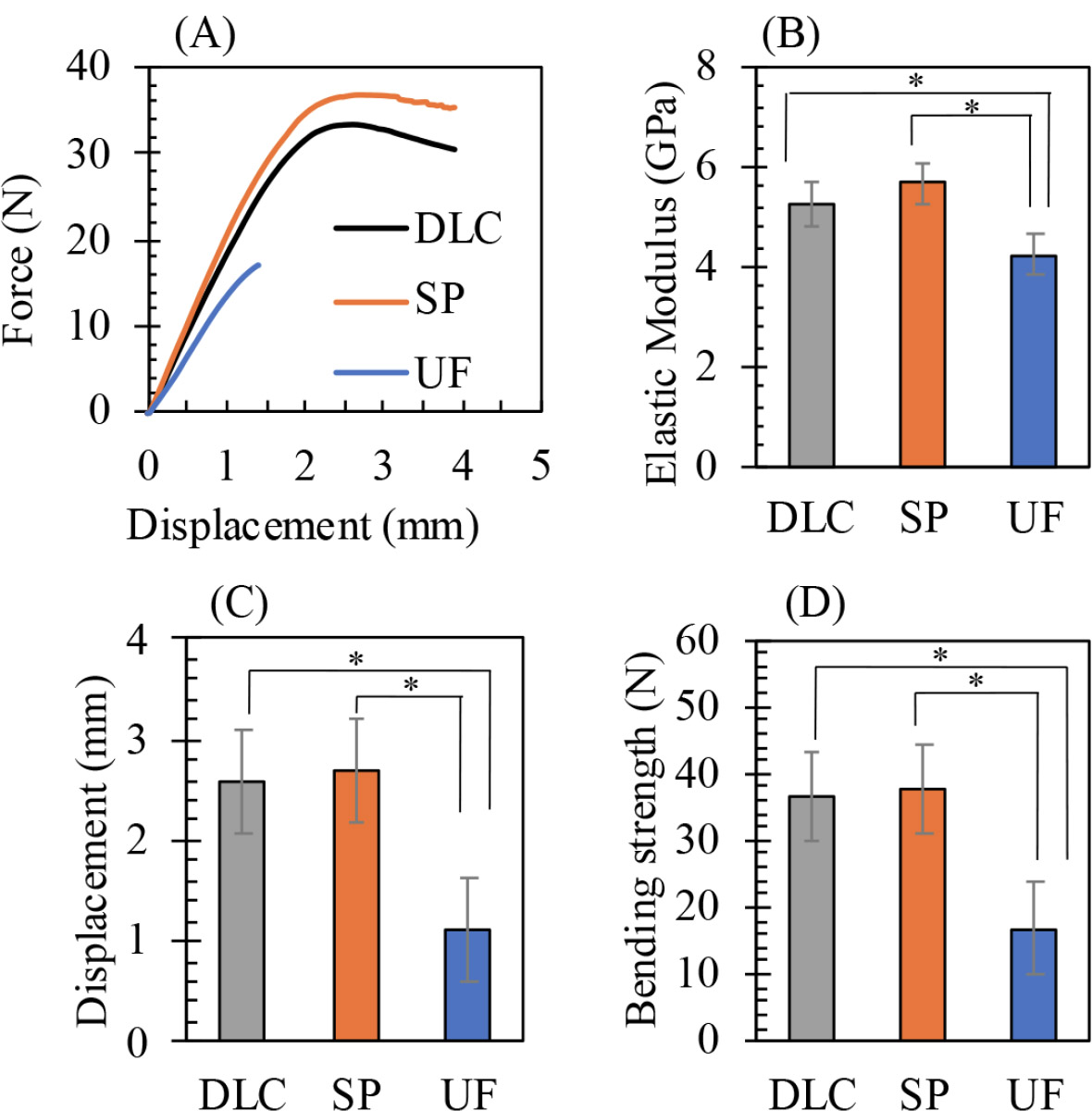
Representative mechanical results of the three-point bending test, including: (A) force–displacement curves (y-axis: force in newtons [N]; x-axis: displacement in millimeters [mm]), (B) elastic modulus values (y-axis: GPa), (C) maximum displacement before failure (y-axis: mm), and (D) bending strength (y-axis: N). DLC: Dental LT Clear; SP: Splint; UF: Uni Fast III. *p < 0.05 indicates statistically significant differences among groups.
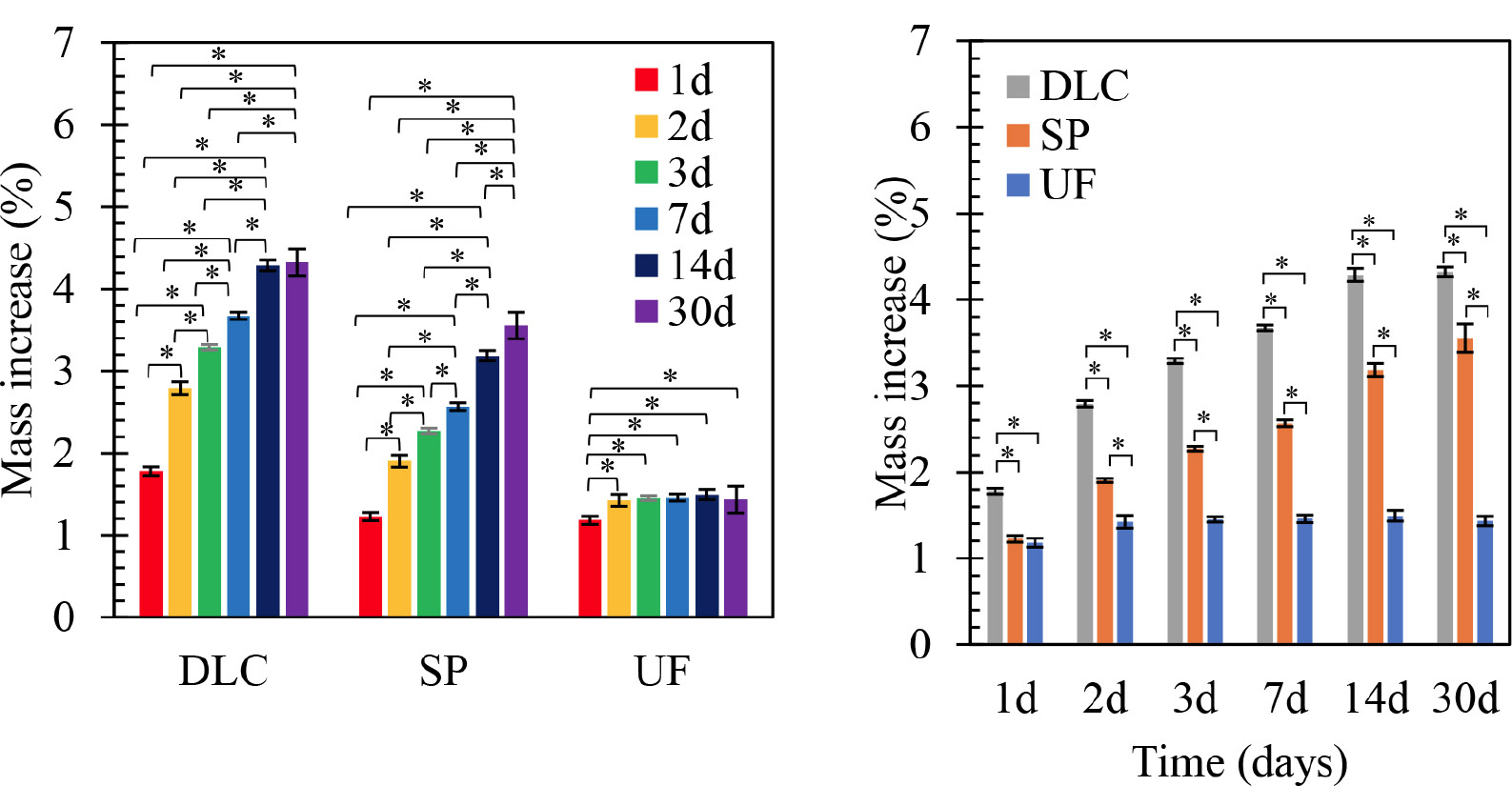
Mean water absorption profiles of the tested materials after immersion for 1, 2, 3, 7, 14, and 30 days. The left panel shows the percentage of mass increase (y-axis) over time (x-axis: days) for each material, while the right panel compares materials at each time point. DLC: Dental LT Clear; SP: Splint; UF: Uni Fast III. *p < 0.05 indicates statistically significant differences among groups and time points.
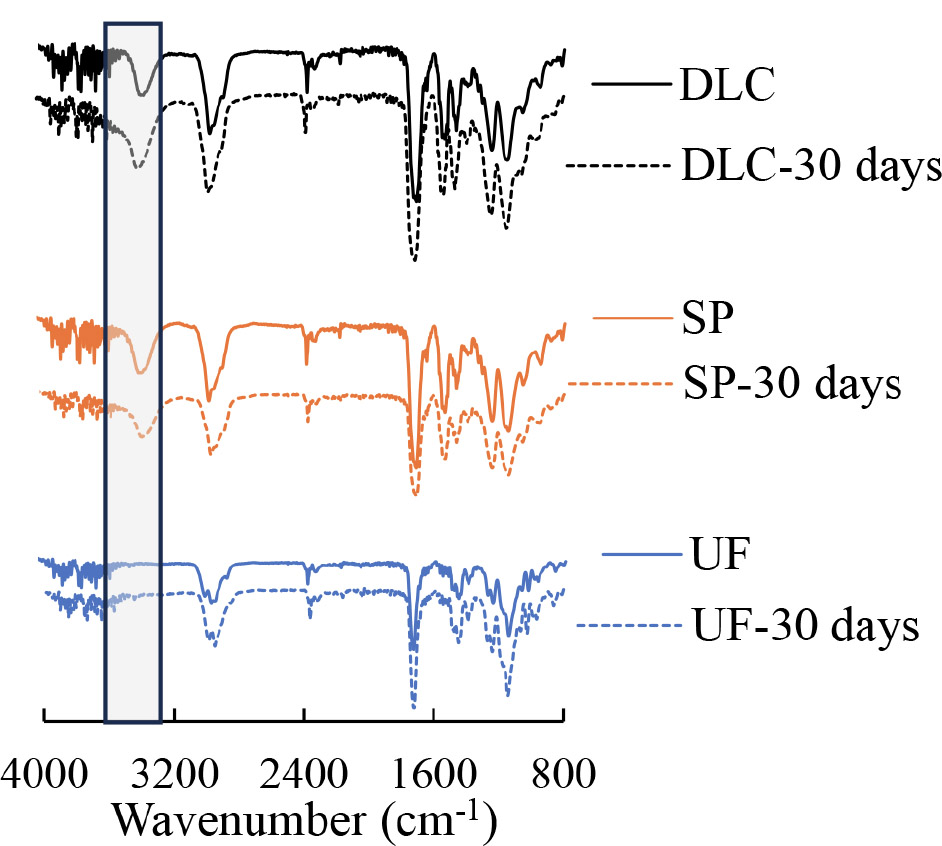
The FTIR spectra of specimens before and after 30 days of immersion in artificial saliva. The x-axis represents the wavenumber (cm−1), and the y-axis represents transmittance (%). The highlighted region at ~3,600 cm−1 reflects changes in the intensity of the hydroxyl (–OH) group absorption band. Solid lines correspond to day 0 and dashed lines to day 30. DLC: Dental LT Clear; SP: Splint; UF: Uni Fast III. *p < 0.05 indicates statistically significant differences.
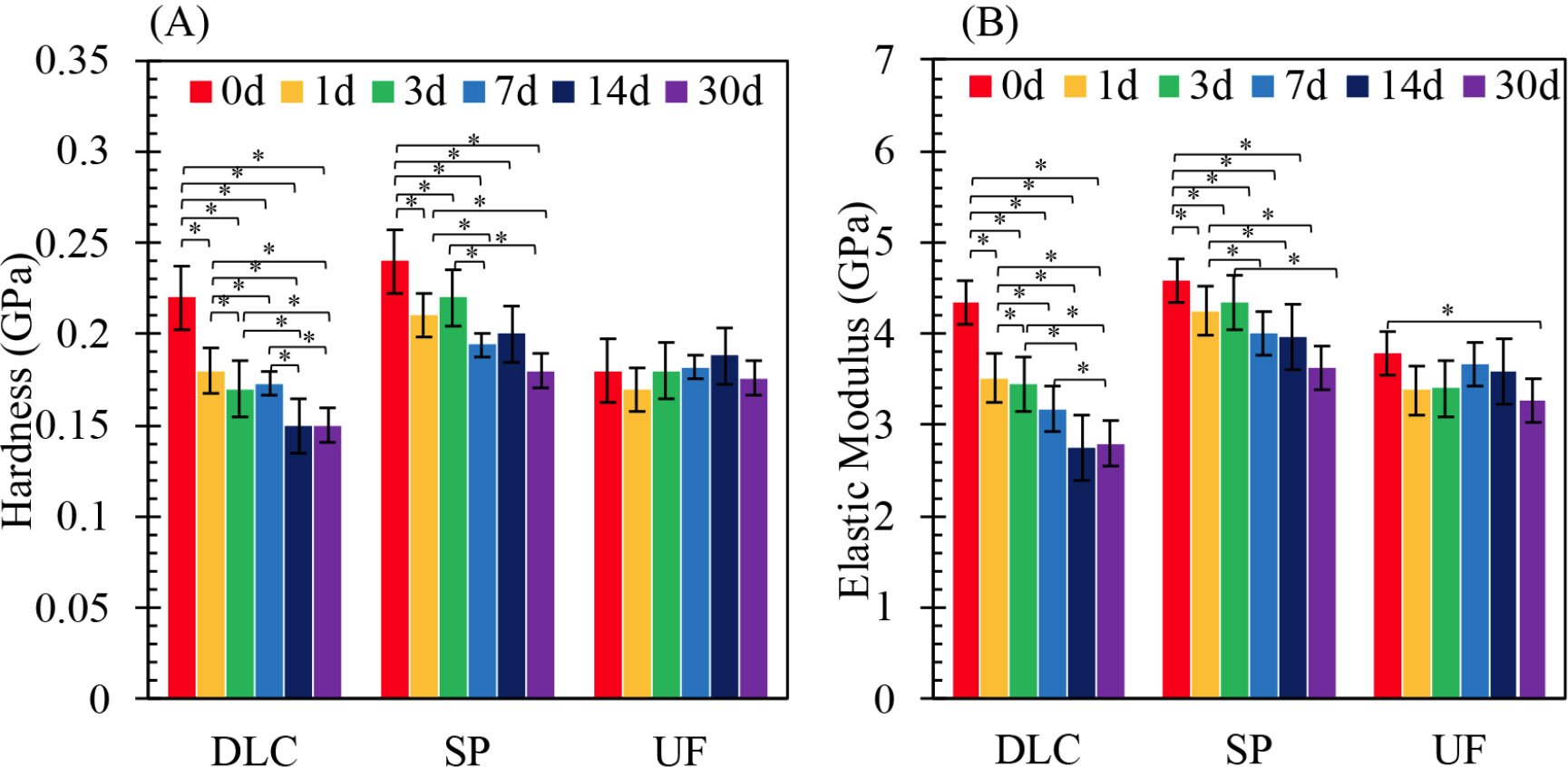
Nanoindentation results showing the mean hardness (A) and elastic modulus (B) values measured at 0, 1, 3, 7, 14, and 30 days. The y-axis shows hardness (GPa) or elastic modulus (GPa), and the x-axis represents the immersion duration (days). DLC: Dental LT Clear; SP: Splint; UF: Uni Fast III. *p < 0.05 indicates statistically significant differences among groups and time points. The mean hardness and elastic modulus values yielded by the nanoindentation test at 1, 2, 3, 7, 14, and 30 days. DLC: Dental LT Clear; SP: Splint; UF: Uni Fast III (*p < 0.05).
4. DISCUSSION
During orthodontic/orthognathic surgery, splints are essential to position the maxilla and mandible precisely during both surgery and initial recovery. The polymeric splint materials must be resistant to possible water-mediated deterioration of the mechanical properties, decomposition, and water absorption in the humid oral environment [15-18]. Therefore, this study examined changes in the physical properties over time, especially water absorption of 3D-printed surgical splint materials.
The elastic modulus, bending strengths, and elongations of both 3D-printing materials revealed by the three-point bending test were similar, and significantly greater than those of conventional PMMA-based resin. The 3D-printing materials would thus be more resistant to stress, especially that generated by the muscles associated with functional mandibular movement [19]. The 3D-printed materials exhibited excellent elongation (ductility); this would reduce the risk of splint chipping during intermaxillary fixation. These findings are similar to those reported by a recent study on 3D-printed denture base resins [20].
However, FTIR revealed that the 3D-printing materials absorbed significantly more water from artificial saliva than did the conventional PMMA-based resin, perhaps reflecting water penetration into the polymer structure; this may be reduced if the printing layers were thinner [20]. Similarly, recent studies evaluating the water absorption of 3D-printing materials, milled and injection materials, or thermoplastic materials have reported that 3D-printed samples exhibited higher water absorption [21, 22]. The correlations between the mechanical properties (hardness and the elastic modulus) of the 3D-printed materials, revealed by the nanoindentation test, and material degradation over time, differed significantly from those of the conventional PMMA-based resin. These results contrast with those of a previous report that examined monomer release in vitro from 3D-surgical splints; such release was less than that from conventional PMMA-based specimens [23]. One possible explanation is that the experiments and materials differed. Of all released monomers, most would be expected to have been surface-located. Our nanoindentation tests quantified the mechanical properties of the surface layer. Further research is needed to clarify the relationship between monomer release and splint mechanical properties.
The results of this study revealed that the 3D-printed materials exhibited significant degradation of mechanical properties upon immersion compared to conventional PMMA-based resin. A recent cohort study on bimaxillary orthognathic surgery reported errors of approximately 0.5 mm in the maxilla and 1 mm in the mandible compared to the designed surgical plan [17]. Considering this error value, the clinical impact of the differences in material properties between the 3D-printed material and PMMA appears to be minimal. However, further prospective comparative studies, such as randomized controlled trials (RCTs), are likely needed to confirm this.
CONCLUSION
Under the conditions of this study, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- The elastic modulus, bending strengths, and elongations of both 3D-printing materials revealed by the three-point bending test were similar and significantly greater than those of conventional PMMA-based resin.
- 3D-printed materials exhibited significantly more water absorption and degradation in artificial saliva than did a conventional PMMA-based resin.
AUTHORS' CONTRIBUTIONS
The authors confirm their contribution to the paper as follows: M.I.: Study conception and design; Y.M., Y.E., K.E. and E.E.Z.: Data collection; Y.M., Y.E., K.E. and E.E.Z.: Data analysis or interpretation; M.I.: Methodology: Y.M. and E.E.Z.: Investigation; M.I.: Draft manuscript. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
| FTIR | = Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| PMMA | = Polymethyl Methacrylate |
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
The data supporting the findings of this study are presented within the article.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank the Chitose Institute of Science and Technology, which is supported by the Nanotechnology Platform Program (Synthesis of Molecules and Materials), for providing the scanning electron microscope.


